How do! / 你好 (nĭ hăo) / Namaste / Welcome!
This week Liverpool F.C. won the Premier League. Well done to them. There has been some boasting [19?] and gloating [mainly aimed at Man Utd and City]. James Milner, now a Champion at Liverpool F.C. had left Manchester City for pastures new and ended up in Anfield. He could have taken a train, car or even a ship to his new club.
Manchester by the Sea may sound like a crap funfair placed by a pond in Heaton Park, but it is actually a title of a movie by Kenneth Lonergan released in 2016. It won awards for acting and stuff like that. It has a soundtrack that doesn’t feature Oasis, The Charlatans or the Happy Mondays. Is it worth seeing? Not a clue. I’ll get round to it, but this movie set in the seaside town, first settled in 1629, of Manchester, Essex County, Massachusetts hasn’t got me yet. No hard feelings Casey Affleck.
Mark Vincent Collins, of The Charlatans, was born in Barton-on-Irwell, which is almost Manchester, but we call it the City of Salford. The Barton Swing Aqueduct allows a canal to pass over a canal. This Roman invention of the Aqueduct was modernised to become a moveable navigable aqueduct. It was a first at the time and many believe it is still the only of its kind. It opened in 1894, year of Manchester City’s naming, and remains working now Built to last by a Derbyshire firm from a plan by Sir Edward Leader Williams. A proper leader he was. So much so, few, if any have followed.
Birmingham may be the city of canals with more miles (56km/35 miles) of canals than Venice (42km/26 miles) but Manchester started the modern canal trend. The Bridgewater Canal runs from Runcorn to Leigh via Manchester. There was no river or stream. It was all dug in deep and long. Since 1761, steamboats, barges and small boats have utilised this modern canal. Used to ferry cotton goods and materials from the sea by Runcorn to Manchester and beyond, and vice versa, the canal was a great innovation. But, after over a hundred years if use it got mucky and couldn’t handle the traffic. Small ships could no longer navigate the near-impassable rivers Mersey and Irwell. The Irish Sea was an awfully long way away.
So, Manchester, faced with the problem of low rainfall, an expensive and limited railway cargo network and rivers ‘hopelessly choked with silt and filth’ (Owen, David, The Manchester Ship Canal, Manchester University Press) removed the barriers. Liverpool’s excessive goods fees had made it cheaper to head east to Hull for goods. That wasn’t good. On October the 7th, 1882 Punch magazine illustrated that Manchester’s idea to bring the sea inland was laughable, “MANCHESTER-SUR-MER. A SEA-DUCTIVE PROSPECT.” Proposals, legal matters and paperwork were underway, and within five years the ground for a new canal was broken.
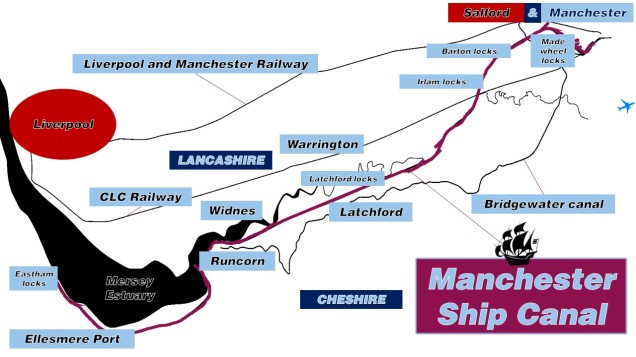
Opened a few days after completion, on the 1st of January 1894, by Queen Victoria, the Manchester Ship Canal was 58km/36 miles long. It is now the 10th longest ship canal in the world. At the time of opening it was second only to the Suez Canal (193km/120 miles) in terms of length for ship canals. Setbacks such as the lead contractor dying, harsh weather, floods (in a dry canal!), and serious money shortages, it was a miracle the canal had been completed. The Pioneer, a steamer, owned by the Cooperative Wholesale Society unloaded sugar that first day. Rouen, Normandy (France) and Manchester were connected and the Stereo MC’s weren’t around to record it.
There’s a great bleak and brown looking landscape by Benjamin Williams Leader (brother of lead engineer Edward Leader Williams) entitled ‘The Excavation of the Manchester Ship Canal: Eastham Cutting with Mount Manisty in the Distance’. Short names for paintings were evidently being rationed around the Long Depression era. The scarred Mount Manisty, Cheshire (a 30m/100’ tall hillock from earth extracted to form the ship canal) sits over the canal in present day and with its coating of trees, it looks to have been there forever. Manchester Liners used to pass this point and their ship the Manchester City, launched on the 27th October 1898.
The oldest proper canal is the Grand Canal of China (大運河 A.K.A. 京杭大運河; Jīng-Háng Dà Yùnhé or the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal). It was started in the 5th century before what is known as the common era. Since then, this now UNESCO World Heritage Site, has ran over 1,794 km (1,115 miles). This Chinese mammoth of a canal is mostly improved rivers, watercourses and some extant diversions of rivers. Merchant Marco Polo, scholar Ibn Battuta, Italian priest Matteo Ricci and Scottish tea-hunter Robert Fortune went to the Grand Canal. The Grand Canal was intended for barges and not shipping.
By comparison, the Panama Canal, opened in 1914. It is 82km long and now is the 8th longest ship canal in the world. The Port of Manchester was once the U.K.’s third-busiest port. Just as the Panama Canals fortunes flagged then raised again, so did Manchester’s Ship Canal. Following slumps from the 1950s to 1960s, the Manchester Ship Canal almost faded away. Nowadays the city’s ship canal ends in Salford and is home to Media City (IV, BBC, Coronation Street, Blue Peter and CBBC), the Imperial War Museum and other leisure facilities, such as The Lowry Centre. You can still take a cruise to the sea – by way of leisure on regular excursion boats (take the Snowdrop from Irlam Locks). The Port of Manchester closed in 1982 and it wasn’t until regeneration kicked in around Salford Quays in the 1990s and then a greater rejuvenation in the decades that follows that the Manchester Ship Canal experienced a new wave of glory.
Far from the times when the Manchester Blitz saw bombs rain down on Trafford, the Manchester Ship Canal and the Port of Manchester, the sights now are much more of green banks and pleasing on the eyes. There’s prosperity around the wharfs, Detroit Swing Bridge, and the National Waterways Museum sits by the Ellesmere Port branch of the Shropshire Union Canal. There’s still a heart beat to the old ship canal yet.
Peel Holdings owns both the Manchester Ship Canal and the Port of Liverpool. Port Salford and the Atlantic Gateway may arrive by the year 2030. The locks, sluices and weirs of the old Manchester Ship Canal are far from closed yet. Ships will continue to sail under the high-level Acton Grange Railway Viaduct, as Network Rail work overhead on the West Coast Main Line, and the dramatic Queen Ethelfleda Viaduct Britannia Bridge (Runcorn Railway Bridge). The linear port has been accessible for over 125 years now and the once nick-named dirty ‘big ditch’dug by navvies is synonymous with the name of Manchester.
In memory of those who died creating the Manchester Ship Canal.